Comprehensive Guide to Kubernetes and OpenShift
Choosing the Right Container Orchestration Platform
Agility and efficiency are critical in the ever-changing context of software development. The capacity to effortlessly deploy, scale, and manage applications has become a defining feature in modern company success. This is where container orchestration, the unsung hero behind the scenes, comes in.
Container Orchestration Unveiled
The skill of automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications is known as container orchestration. Containers have transformed how applications are packaged, making them portable and consistent across environments. However, Kubernetes and OpenShift come into play when efficiently orchestrating these containers.
These two container orchestration titans have earned their stripes for good reason. They enable enterprises to fully utilize the capabilities of containers by simplifying complicated procedures and creating a consistent, resilient, and scalable application environment.
Why Kubernetes and OpenShift?
Kubernetes and OpenShift are two names that stand out in the world of container orchestration. Kubernetes, which was formed from the Google empire, has become the gold standard for container orchestration due to its open-source nature and a strong community that is constantly improving its capabilities. OpenShift, on the other hand, is developed by Red Hat and takes Kubernetes to the enterprise level, stacking it with features and support suitable for enterprises of all kinds.
But why should you be interested in these platforms as a developer, operator, or company leader? The answer is simple: they enable you to seamlessly manage your apps, grow with confidence, and embrace a cloud-native strategy. In this comprehensive tutorial, we'll look at both Kubernetes and OpenShift, allowing you to make an informed decision that corresponds with your needs.
A Journey of Exploration Awaits
We'll go deep into both Kubernetes and OpenShift in this book, leaving no stone unturned. You'll obtain a thorough understanding of how these platforms work, their distinct advantages, and when to favor one over the other. Whether you're a seasoned DevOps engineer or just getting started with container orchestration, this article is here to help.
In the following sections, we'll deconstruct the fundamentals of container orchestration, deconstruct Kubernetes and OpenShift, set up your clusters, and start on hands-on trips to deploy and manage applications. By the end of this detailed guide, you will be able to select the best container orchestration platform for your requirements.
Understanding Container Orchestration
The world of container orchestration can appear intimidating at first, especially if you're unfamiliar with the concept. In this section, we'll go over the principles of container orchestration and why it's such a big changer for modern software development.
What is Container Orchestration?

Container orchestration, at its most basic, is the technique of automating the deployment, scaling, and administration of containerized applications. Containers, such as those generated with Docker, have completely changed the way we package and operate applications. They enclose an application and its dependencies, ensuring consistency and portability across environments ranging from development laptops to production servers.
Container orchestration extends this by offering a framework for managing containers efficiently. It tackles duties such as:
Deploying containers to multiple hosts.
Ensuring containers are always up and running.
Scaling containers based on demand.
Load balancing traffic to containers.
Managing storage and network configurations.
Rolling out updates and changes seamlessly.
The goal is to free developers and operators from the complexities of manual management, allowing them to focus on building and improving applications.
Why Container Orchestration Matters
In today's fast-paced world of software development, container orchestration is not just a convenience but a necessity. Here's why it matters:
Scalability: Container orchestration platforms make it easy to scale applications up or down, ensuring they can handle varying workloads without manual intervention.
High Availability: By distributing containers across multiple hosts, orchestration platforms enhance the availability of applications. If one host fails, containers can be rescheduled elsewhere.
Resource Optimization: Orchestration optimizes the utilization of resources, ensuring that containers run only where needed, reducing infrastructure costs.
Simplified Management: It simplifies complex tasks like deployment, updates, and load balancing, freeing up human resources for more valuable activities.
Cloud-Native Approach: Container orchestration aligns with the principles of cloud-native computing, making applications more adaptable to dynamic cloud environments.
Kubernetes In-Depth

Let's dig into the world of Kubernetes now that we've demonstrated the necessity of container orchestration. Kubernetes, sometimes known as K8s, is an open-source container orchestration platform that has become the industry standard. In this section, we'll go deep into Kubernetes, learning about its key concepts and why it's a top choice for container orchestration.
Introduction to Kubernetes
Kubernetes, also known as K8s (pronounced "K-8s"), was created by Google and later donated to the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF). It is intended to automate containerized application deployment, scalability, and management. But what distinguishes Kubernetes?
Origin: Kubernetes boasts an impressive lineage, born from Google's experience in managing containers at scale. It carries the DNA of Google's internal container orchestration system, Borg.
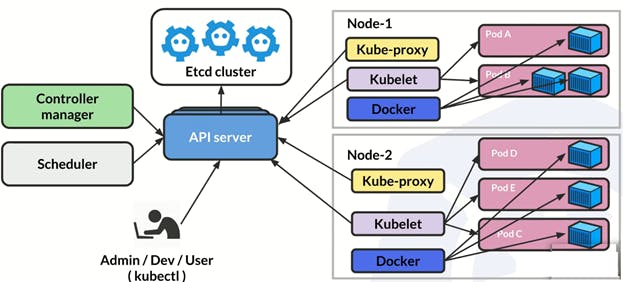
Architecture: At its core, Kubernetes employs a master-slave architecture. The master node oversees the cluster and manages its state, while worker nodes execute tasks and host containers.
Components: Kubernetes consists of several components, each with specific roles. These include the control plane components (API server, etcd, controller manager, and scheduler), as well as nodes that run containers (Kubelet and Kube Proxy).
Key Features and Benefits
Kubernetes offers a rich set of features that make it an attractive choice for container orchestration:
Orchestration: Kubernetes automates container deployment, scaling, and management, simplifying complex tasks.
Scalability: It scales horizontally to accommodate growing workloads by adding more containers when needed.
Self-Healing: Kubernetes ensures that containers are always running. If a container fails, it's rescheduled automatically.
Load Balancing: The platform intelligently distributes traffic to containers for optimal performance.
Storage Orchestration: It manages storage volumes, making it easy to mount storage solutions to containers.
Rolling Updates: Kubernetes allows you to roll out updates to applications without downtime.
Declarative Configuration: You describe the desired state of your application, and Kubernetes ensures it matches that state.
Setting Up Kubernetes
In this section, we'll provide you with a detailed guide on setting up Kubernetes, from preparing your environment to deploying your first application.
1. Choose Your Environment
Local Development: Minikube
Minikube is a tool that enables you to run a single-node Kubernetes cluster on your local machine. It's a great choice for development and testing.
- Installation: To install Minikube, follow the instructions provided in the official documentation for your operating system. You can typically install it using package managers like
brewon macOS orchocolateyon Windows.
Production Environment: Managed Kubernetes Service
For a production environment, consider using a managed Kubernetes service from a cloud provider. Options include Amazon EKS, Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), and Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
2. Install Dependencies
Ensure that you have the following dependencies installed:
Docker: Install Docker to build and run containerized applications.
kubectl: The Kubernetes command-line tool allows you to interact with your cluster.
Hypervisor: If you're using Minikube on macOS or Windows, you'll need a hypervisor like VirtualBox or Hyper-V.
3. Setting Up Minikube (Local Development)
For Minikube, you can set up your local Kubernetes cluster as follows:
# Start Minikube
minikube start
# Verify that Minikube is running
minikube status
# Deploy your first application (example: nginx)
kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx
# Expose the deployment as a service
kubectl expose deployment nginx --type=NodePort --port=80
You can access your application using the provided NodePort.
4. Setting Up Managed Kubernetes (Production Environment)
For a production environment, refer to the documentation of your chosen managed Kubernetes service for detailed setup instructions. You'll typically need to create a cluster, configure network settings, and set up authentication and access control.
OpenShift In-Depth
Kubernetes is the open-source juggernaut in the world of container orchestration. However, there is another challenger, similarly powerful and with a distinctive twist: OpenShift. Red Hat's OpenShift platform enhances Kubernetes for enterprise success. In this section, we'll dig deeper into OpenShift, learning about its core concepts, essential features, and why it's a top choice for enterprises.
Introduction to OpenShift
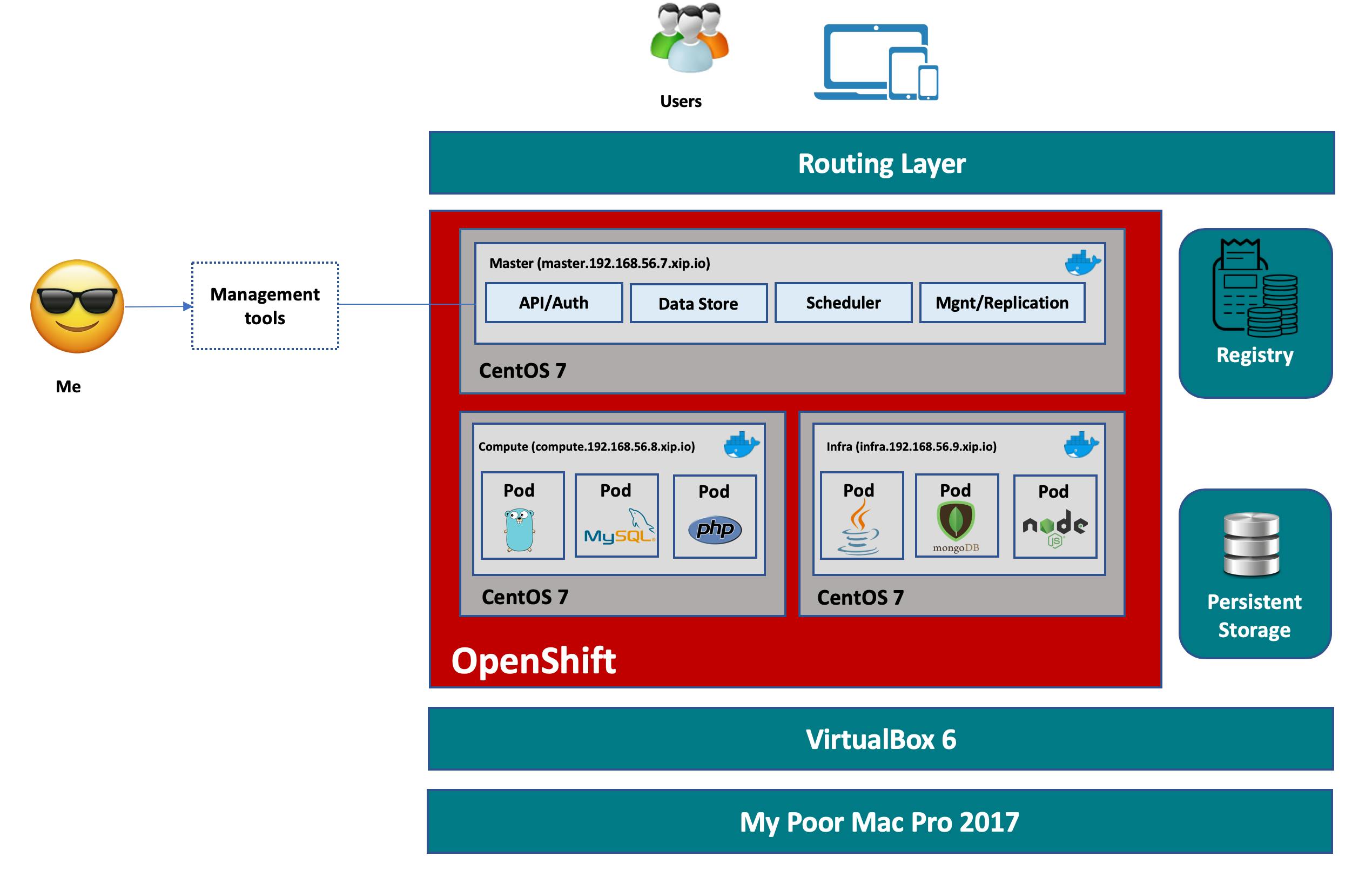
OpenShift is a Kubernetes-based container orchestration platform that places a significant emphasis on enterprise-grade features. What sets OpenShift apart?
Enterprise Focus: OpenShift is tailored for businesses, with features designed to address the unique requirements of enterprises.
Developer Productivity: It empowers developers with a rich set of tools and an integrated development environment.
Unified Operations: OpenShift streamlines operations by providing a consistent platform for deploying and managing containerized applications.
Security and Compliance: OpenShift prioritizes security and compliance, offering a robust solution for sensitive environments.
Key Features and Benefits
OpenShift offers a range of features and benefits that cater to enterprise needs:
Source-to-Image (S2I): OpenShift simplifies the build process with S2I, allowing developers to go from source code to container images with ease.
Developer-Friendly: It provides a developer-friendly environment with integrated tools, making it easy to build, test, and deploy applications.
Multi-Tenancy: OpenShift supports multi-tenancy, allowing different teams or projects to share the same cluster securely.
Service Catalog: The platform includes a service catalog for discovering and provisioning services like databases and messaging systems.
Policy-Based Access Control: OpenShift offers fine-grained access control, essential for enterprise security and compliance.
Monitoring and Logging: It includes built-in monitoring and logging capabilities, ensuring the health and performance of applications.
Setting Up OpenShift
In this section, we'll provide a detailed guide on setting up OpenShift, whether you're using it for local development or in a production environment.
1. Choose Your Environment
Local Development: CodeReady Containers
CodeReady Containers is designed for local development and testing with OpenShift. It provides a lightweight OpenShift cluster.
- Installation: Download the CodeReady Containers distribution for your operating system and follow the installation instructions provided.
Production Environment: Red Hat OpenShift
For a production-ready OpenShift environment, consider using Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform. This involves a more complex setup process and may require a Red Hat subscription.
2. Install Dependencies
Ensure that you have the following dependencies installed:
Docker: Install Docker to build and run containerized applications.
oc (OpenShift command-line tool): Download and install the oc tool from the OpenShift website.
3. Setting Up CodeReady Containers (Local Development)
For CodeReady Containers, you can set up your local OpenShift cluster as follows:
# Start CodeReady Containers
crc start
# Log in to the OpenShift cluster
crc oc-env | Invoke-Expression
oc login -u developer -p developer
4. Setting Up Red Hat OpenShift (Production Environment)
Setting up Red Hat OpenShift for production is a more complex process that involves purchasing licenses and configuring a cluster. Please refer to Red Hat's official documentation for detailed instructions based on your specific use case.
Deploying Your First Application
In this section, we'll guide you through deploying your first application on both Kubernetes and OpenShift.
Kubernetes: Deploying Your Application
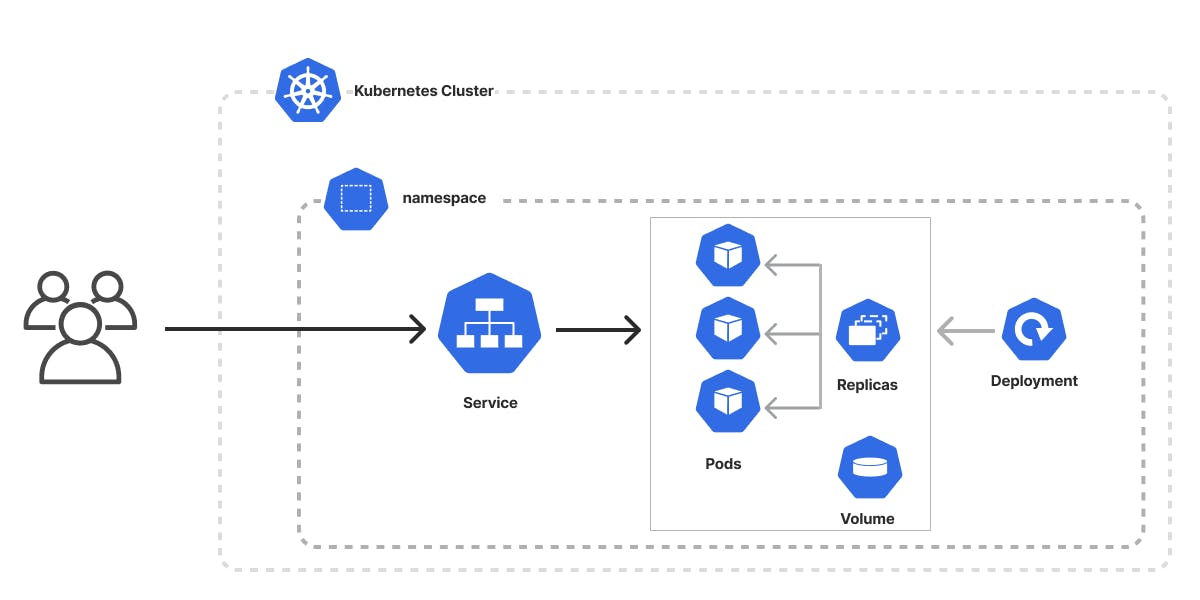
- Create a Kubernetes Deployment YAML: Create a YAML file for your deployment configuration. Here's an example of a simple NGINX deployment:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
- Apply the Deployment Configuration: Apply the deployment configuration to your Kubernetes cluster using
kubectl:
kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
- Expose the Deployment: Expose the NGINX deployment as a NodePort service:
kubectl expose deployment nginx-deployment --type=NodePort --port=80
You can access your NGINX application via the NodePort.
OpenShift: Deploying Your Application
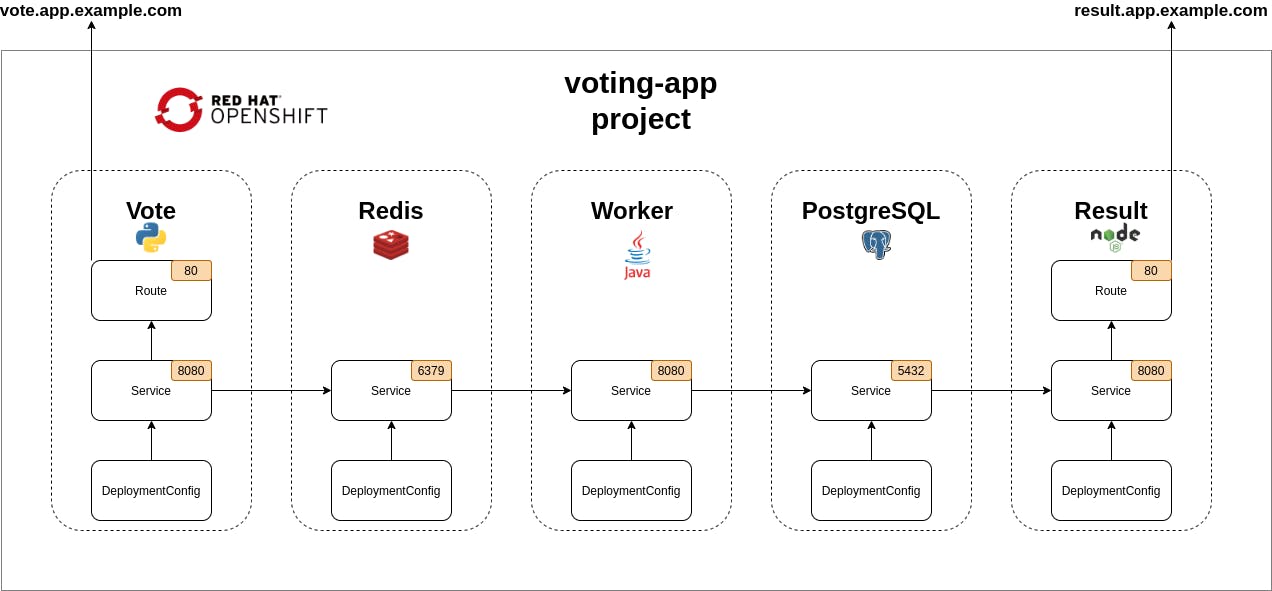
Create an OpenShift Deployment YAML: Create a YAML file for your deployment configuration in OpenShift. The process is similar to Kubernetes but may include additional OpenShift-specific settings.
Apply the Deployment Configuration: Apply the OpenShift deployment configuration using
oc:
oc apply -f your-app-deployment.yaml
- Expose the Deployment: Expose your application deployment using OpenShift routes. For example:
oc expose svc your-app-service
You can access your application through the generated route.
Comparative Analysis

In this section, we'll perform a detailed comparative analysis of Kubernetes and OpenShift, covering various aspects such as features, benefits, and use cases.
Balancing Flexibility and Out-of-the-Box Efficiency
Kubernetes:
Offers high flexibility, allowing users to configure and manage every aspect of their clusters.
Requires more manual setup and configuration.
Ideal for users who need complete control over their environments.
OpenShift:
Strikes a balance between flexibility and ease of use, providing more opinionated defaults.
Comes with built-in features that simplify application deployment and management.
Suitable for users who want a smoother out-of-the-box experience.
Weighing Community-Driven Innovation Against Enterprise Features
Kubernetes:
Driven by a large open-source community with constant innovation.
Offers a wide range of plugins, extensions, and third-party integrations.
Ideal for organizations looking for a rich ecosystem of tools.
OpenShift:
Incorporates Kubernetes as its foundation while adding enterprise-grade features.
Focuses on security, compliance, and stability.
Suitable for businesses with strict compliance and security requirements.
DIY Approach Versus Integrated Operations
Kubernetes:
Requires more manual configuration and setup.
Offers more control but can be complex to manage.
Best suited for users who are comfortable with hands-on cluster management.
OpenShift:
Provides integrated solutions for common operational tasks.
Simplifies deployment, scaling, and updates.
Beneficial for organizations that want a more streamlined operational experience.
Navigating Between a Broad Ecosystem and Developer Productivity Tools
Kubernetes:
Offers a vast ecosystem of tools and resources for various use cases.
Requires users to choose and integrate these tools based on their needs.
Ideal for users who require specific tools and have the expertise to integrate them.
OpenShift:
Focuses on developer productivity with integrated tools.
Provides features like source-to-image (S2I) to simplify the development process.
Suitable for businesses looking to improve developer efficiency.
Evaluating Open-Source Roots Versus Security and Compliance Focus
Kubernetes:
Maintains a strong open-source ethos with a transparent development process.
Relies on community-driven security practices.
Suitable for organizations that prioritize open-source solutions.
OpenShift:
Integrates Kubernetes with additional features for security and compliance.
Offers enterprise-level support and security features.
Ideal for businesses that require strong security and compliance standards.
Conclusion
In the conclusion, we summarize the key insights from our comparison of Kubernetes and OpenShift and guide for making an informed decision.
Tailoring Choices to Organizational Needs
The decision between Kubernetes and OpenShift ultimately depends on your organization's specific requirements. Consider factors like the level of control, desired security and compliance features, and developer productivity tools that align with your goals.
Acknowledging the Dynamic Evolution of Container Orchestration
Container orchestration is a dynamic field, continually evolving with new features and capabilities. Staying updated with the latest advancements in Kubernetes and OpenShift is crucial for making informed decisions.
Final Insights to Steer Informed Decision-Making
Kubernetes offers unparalleled flexibility, best suited for users who require complete control and are comfortable with manual setup. It shines in a diverse ecosystem of tools and plugins.
OpenShift provides a balance between flexibility and integrated operations. It excels in enterprise-grade features, security, and compliance, making it ideal for organizations with strict requirements.
Ultimately, your choice should align with your specific use case, organizational priorities, and expertise. The right platform empowers you to effectively manage containerized applications and meet your business objectives.

